The prevalence of substance use disorder and mental health disorder in the US.
Substance Abuse and Mental Health
Substance abuse and Mental health | Table of Contents
Prevalence of Substance Use Disorder and Mental Health Disorder
Certain individuals tend to suffer from both a substance use disorder, such as alcohol addiction or drug addiction, and a mental health disorder, such as depression or anxiety simultaneously. This condition is known as dual diagnosis, comorbidity, or co-occurring disorder and is a relatively new field of study. While substance abuse is recognized as mental health disorder on its own, it is also a condition that triggers the development of other mental health conditions.
Mental health and substance use disorders affect individuals from all walks of life, age groups, ethnicity, and all socioeconomic backgrounds. These illnesses are common, recurrent, and often serious but are treatable when they are addressed and treated separately. Mental disorders involve changes in the way a person thinks, their mood, and behavior. While there remains a direct link between substance use disorder and mental health disorder, there is no definitive way to identify what occurred first. However, the fact that they tend to aggravate the condition of both disorders is apparent.
Key Statistics
According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), about 45 percent of Americans suffer from both a substance use disorder and mental health condition.
- About 4 million Americans over the age of 18 had both a substance use disorder and mental health condition in 2001.
- According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), about 1.4 percent of adolescents and 4.2 percent of adults had a dual diagnosis in 2013.
- According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), nearly 7.7 million adults had both a substance use disorder and mental health condition in 2017.
- Of the 20.3 million adults with substance use disorders in 2017, approximately 37.9 percent also had a mental health condition.
- Of the 42.1 million adults with mental illnesses in 2017, about 18.2 percent also had a substance use disorder.
- According to the NSDUH, about 9.5 million American adults had a dual diagnosis in 2019.
- More than 60 percent of adolescents in community-based substance abuse treatment programs had symptoms of another mental illness.
- According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), the percentage of adults with both a substance use disorder and mental health disorder has been gradually increasing from 2015 through 2018.
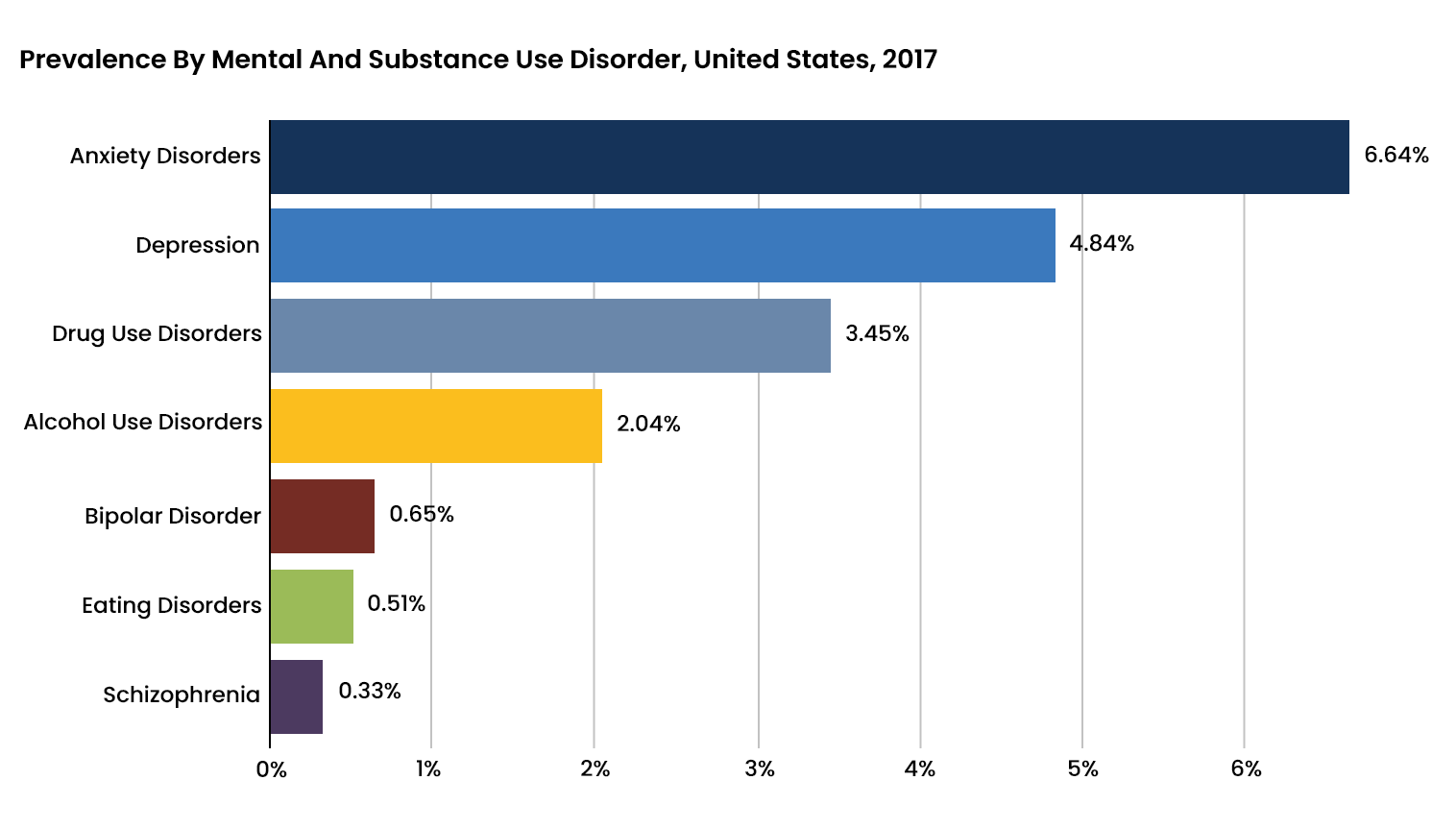
Prevalence of Substance Use in People with Mental Health Disorders
Comorbidity can sometimes occur when individuals start abusing alcohol or drugs to alleviate the symptoms of a mental health condition. Although such use of alcohol or drugs may relieve the symptoms of a mental health condition temporarily, it tends to aggravate both conditions in a matter of hours that leads to a vicious cycle of abuse.
- Individuals with a mental health condition are twice as likely to develop a substance use disorder. About 1 in 4 individuals with a serious mental illness also have a substance use disorder.
- The percentage of adults with mental health conditions who proceeded to develop substance use disorders has steadily increased from 2008 to 2014.
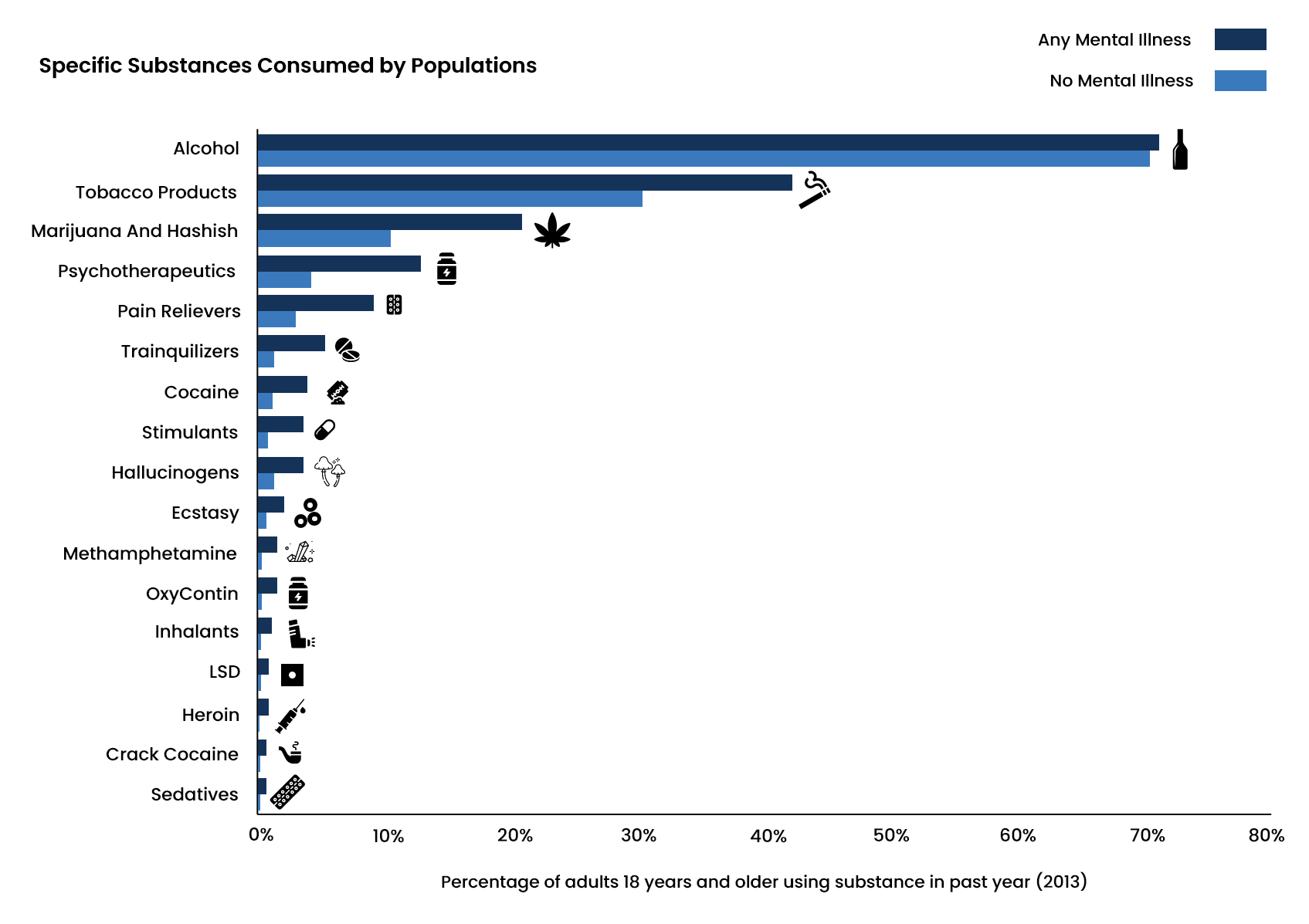
- Individuals with mental health disorders were about four times more likely to be heavy alcohol users, 3.5 times more likely to use marijuana daily, and 4.6 times more likely to use other drugs.
- More than 70 percent of adults with mental illnesses abused alcohol in 2013, while around 20 percent of adults with mental illnesses abused marijuana.
- Around 68.1 percent of individuals with a serious mental illness abused marijuana in 2018.
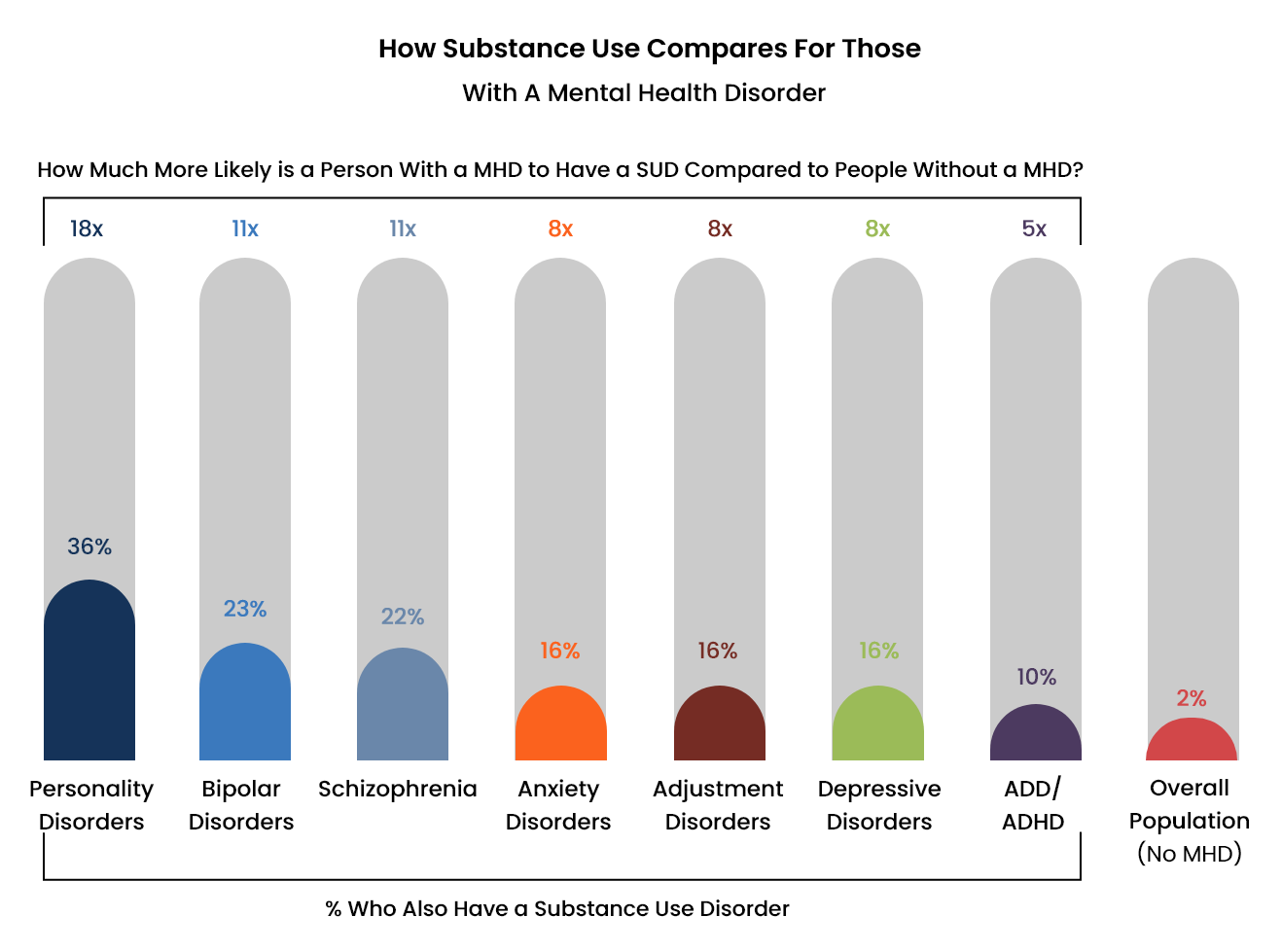
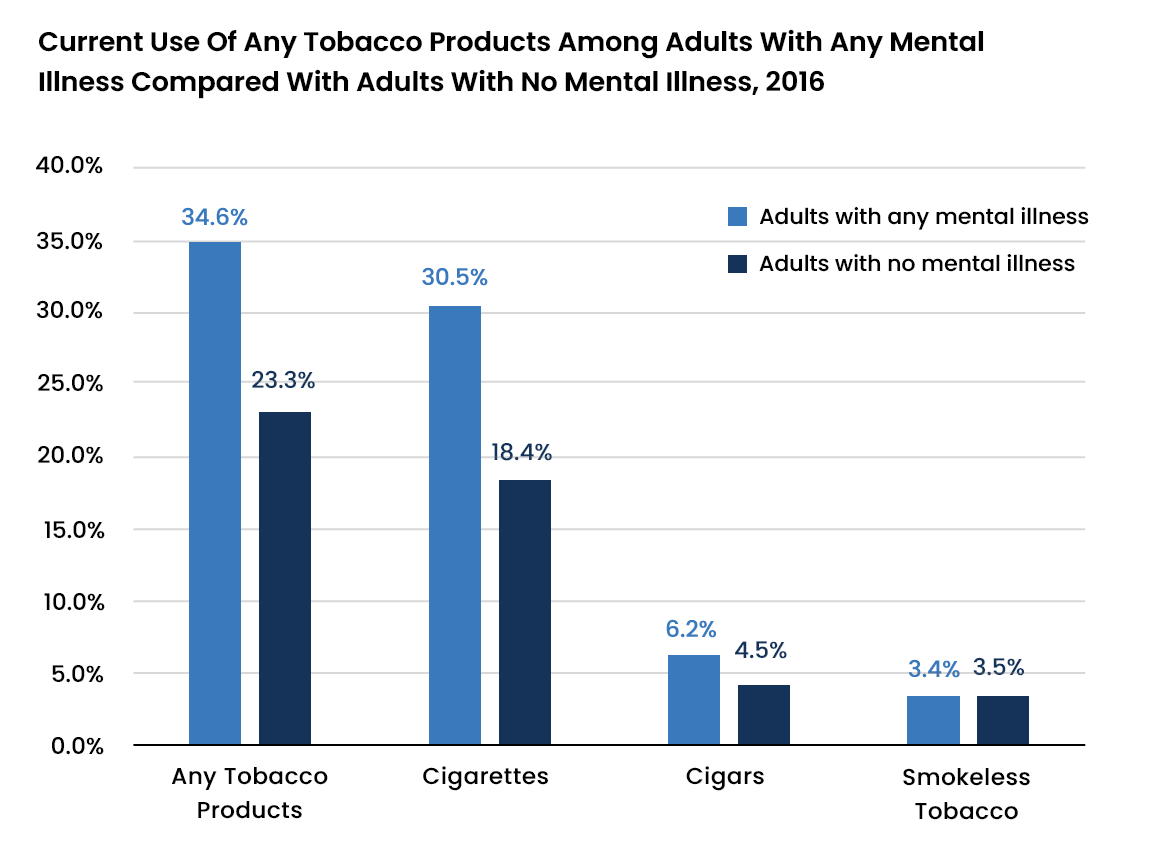
Smoking and Mental Health Disorder
Studies have revealed a link between tobacco use and mental health disorders. Individuals with mental health disorders, such as depression, schizophrenia, and panic disorders, are highly likely to smoke tobacco as compared to the general population.
- According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Americans with mental illnesses are 70 percent more likely to smoke tobacco than the general population.
- According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), individuals with mental health conditions smoke two to three times more tobacco than the general population.
- From 2009 to 2011, around 36.1 percent of individuals with mental illnesses smoked tobacco than the 21.4 percent with no mental illnesses.
- Tobacco use is particularly high among individuals with serious mental illnesses. According to estimates, about 70 to 85 percent of individuals with schizophrenia and 50 to 70 percent of individuals with bipolar disorders smoke tobacco on a regular basis.
- According to data derived from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) from 2008 to 2012, adults with mental illnesses consumed 8.7 percent of all cigarettes sold, although they accounted for only 6.9 percent of past-month smokers.
- According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), the past month cigarette use among individuals with mental illnesses was the highest in 18 to 25-year-olds and lowest in 50 years and older from 2012 to 2014.
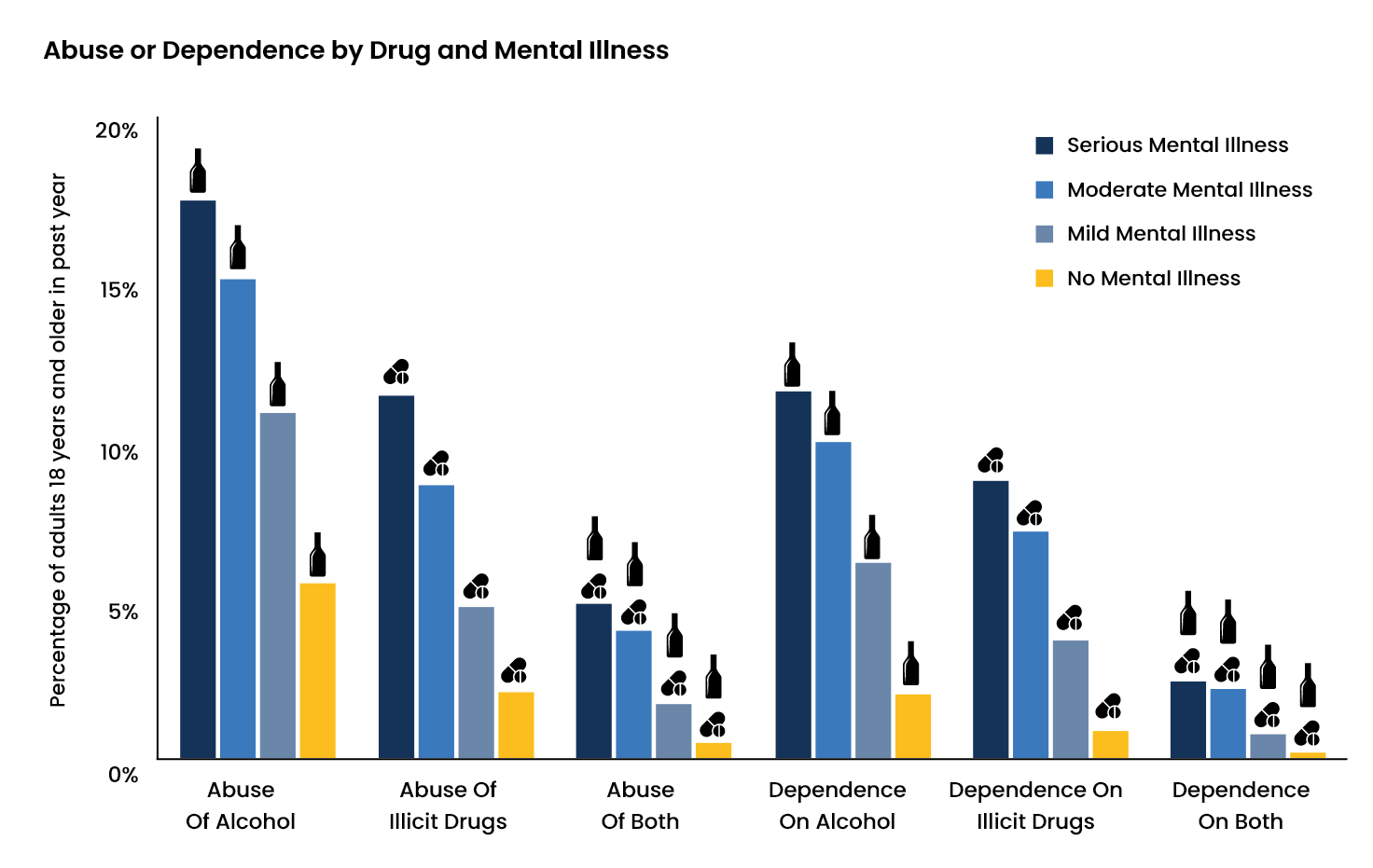
Comorbidity and Alcoholism
Certain individuals tend to abuse alcohol in hopes of relieving the symptoms of a mental health condition. Although such consumption of alcohol may temporarily relieve the symptoms of the mental illness, it may worsen them in the long-run and result in the development of comorbidity.
- Approximately 19 percent of the US adult population suffers from both an alcohol use disorder and mental illness.
- According to reports published by the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), about 37 percent of individuals with alcohol use disorders also have a comorbid mental health condition.
- According to the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), individuals with mental illnesses consume about 38 percent of all alcohol distributed.
- In 2012, almost 60 percent of patients in treatment facilities had both an alcohol use disorder and a mental illness.
- Around 3.6 to 26 percent of homeless adults suffered from both a mental illness and alcohol use disorder in 1990.
- According to the Epidemiologic Catchment Area (ECA) study, about 33.7 percent of individuals with schizophrenia and 42.6 percent of individuals with bipolar disorders also met the alcohol use disorder criteria in 1990.
Illicit Drug Abuse Among Mental Health Patients
Certain individuals may turn to illicit drugs, such as cocaine, heroin, or marijuana, in an attempt to self-medicate the symptoms of a mental illness, eventually developing a co-occurring disorder.
- In 2019, about 15.3 percent of adults with serious mental illnesses and 8.9 percent of adults with any mental illnesses also suffered from an illicit use disorder.
- In 2013, illicit drug use among adolescents aged 12 to 17 was higher in those who had a major depressive disorder (33 percent) as compared to those without a major depressive disorder (15.2 percent).
- In 2017, about 40.4 percent of adults with severe mental illnesses and 36.7 percent of adults with any mental illnesses reportedly used illicit drugs.
- In 2018, about 40.4 percent of adults with serious mental illnesses and 38.8 percent of adults with any mental illnesses reportedly used illicit drugs.
- Around 31.9 percent of illicit drug users aged 12 to 17 in 2019 reportedly had a major depressive disorder the previous year.
Statistics on Emergency Room Visits
Individuals with a dual diagnosis may sometimes require immediate medical attention to treat the complications that arise from both conditions.
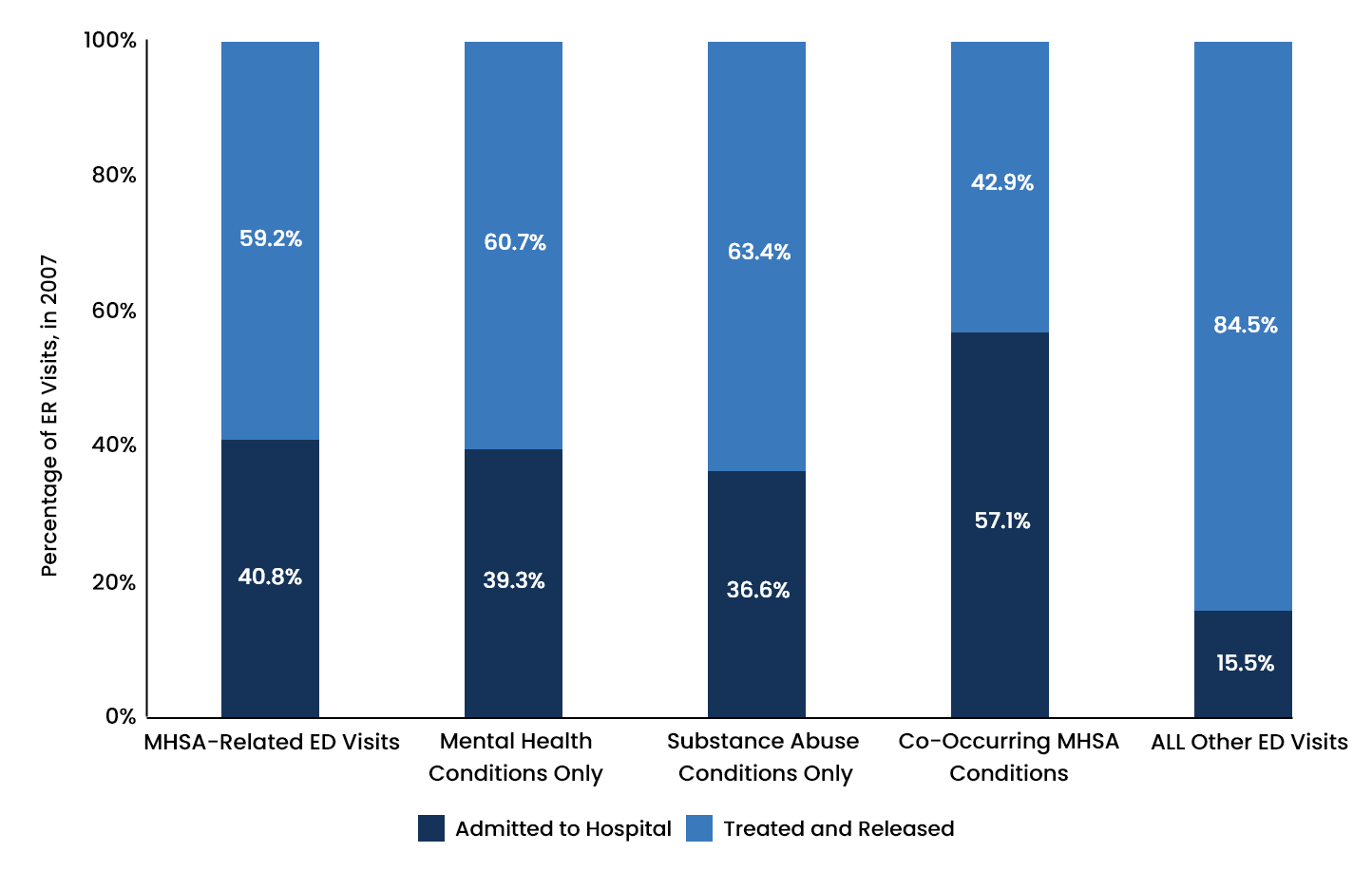
- Emergency room visits related to co-occurring disorders accounted for about 11.9 percent of all ER visits. This accounts for over 4.1 million ER visits in 2007.
- Emergency room visits related to comorbidities were two and a half times more likely to result in hospitalization.
- Emergency room visits related to co-occurring disorders were significantly higher in 18 to 44-year-olds. In 2007 alone, around 58.8 percent of ER visits for co-occurring disorders involved this age group.
- Emergency room visits related to co-occurring disorders in men were around 57 percent in 2007.
- Between 1997 and 2010, around 0.4 percent of emergency room visits involving adolescents were related to co-occurring disorders.
- Between 1997 to 2010, around 20.9 percent of emergency room visits related to substance abuse by adolescents were reportedly complicated by a mental health condition.
Recovery Statistics
There are many treatment options currently available to treat both substance use disorder and mental health conditions simultaneously. Rehab facilities are increasingly adopting comprehensive approaches to address various types of co-occurring disorders. However, only a few ever seek treatment or receive adequate treatment.
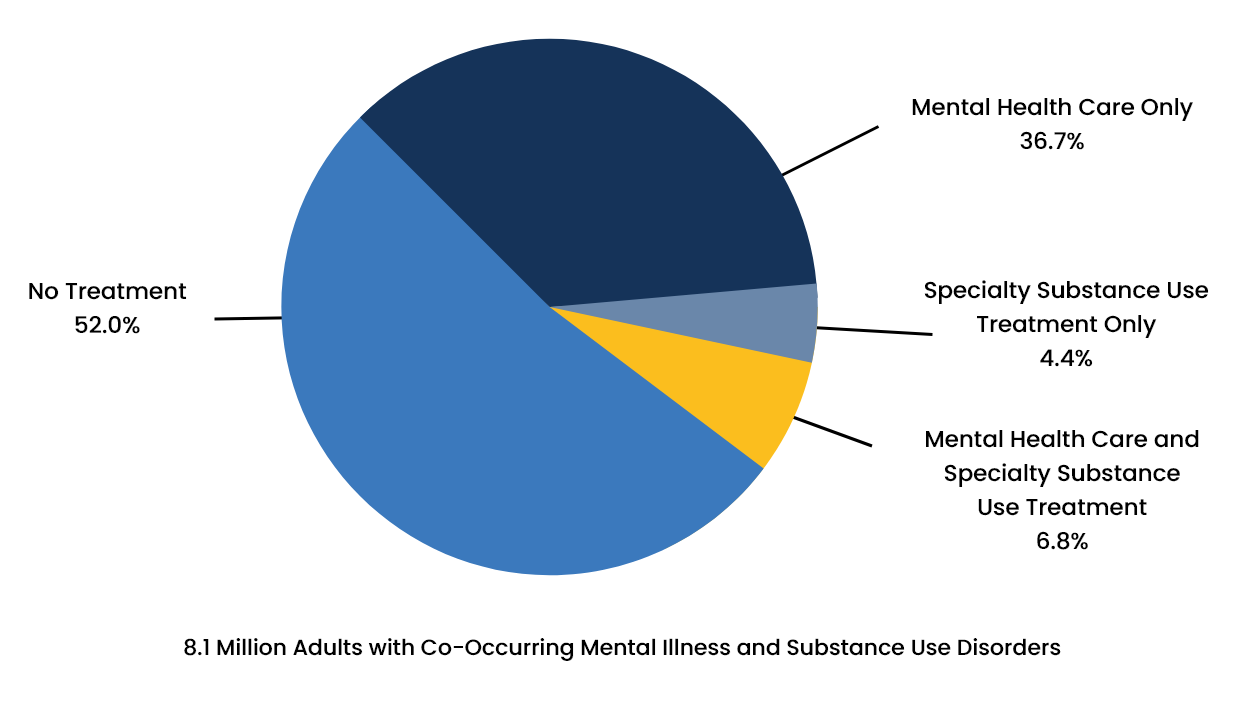
- An estimated 52 percent of individuals with co-occurring disorders receive neither substance abuse nor mental care treatment.
- Around 36.7 percent of individuals with co-occurring disorders receive only mental care treatment, while around 4.4 percent receive only substance abuse treatment.
- Only about 6.8 percent of those with co-occurring disorders receive treatment for both the mental health condition and substance use disorder.
- In 2016, about 48.1 percent of adults with co-occurring disorders received treatment for one of the conditions at a specialty facility, while only a small proportion of 6.9 percent received treatment for both the disorders.
- Between 1980 to 1990, about 50 to 70 percent of patients receiving substance abuse treatment showed histories of co-occurring disorders, while around 20 to 50 percent of adults receiving treatment for mental illnesses showed a history of substance use disorders.
- In 2005, nearly 6.6 percent of adults with co-occurring disorders involving any mental illnesses and 15.5 percent of adults with co-occurring disorders involving serious mental illnesses received treatment.
Recovery Partner Network
We aim to educate and empower. If you feel our library of resources does not cover your specific need, reach out to us, and we would be happy to help.
STATISTICS
© Copyright 2026


